The quality of a video call can truly make or break a meeting. Poor video quality is not only frustrating, but it can limit productivity and keep you from reaching your goals. experiencing recurring jitter or lags or freezes. Did you know that 60% of Zoom issues are caused by poor internet? The good news is it can usually be fixed. Here are some common troubleshooting steps you can take to improve your connection.
Check your Wi-Fi Speed
Your network speed is the most obvious cause of poor connectivity in video meetings. Zoom and Teams both recommend a bandwidth speed of around 4.0Mbps upload and download. If you’re having connection issues, the first recommended step is to check your internet speed by running a speed test. Speedtest.net is probably the most well-known site.
Based on your results, you will know if high-quality video calling is possible over your current connection. The following speeds are recommended when using Zoom:
For 1:1 video calling:
- 720p HD video: 1.2Mbps (up/down)
- 1080p HD video: 3.8Mbps/3.0Mbps (up/down)
For group video calling:
• 720p HD video: 2.6Mbps/1.8Mbps (up/down)
• 1080p HD video: 3.8Mbps/3.0Mbps (up/down)
Zoom themselves say the bandwidth used will be optimised for the best experience based on your network. It will automatically adjust for 3G, Wi-Fi, or wired connections so you don’t need to choose which one to use.

Choose the right Wi-Fi bandwidth
Slow connections can be caused by interference in the Wi-Fi signal, or by obstacles between the router and the device. Switching to a different bandwidth can help with this.
If your network has 2 bandwidth options, choose the best one based on the layout of your home or workplace. You can usually choose between 2.4GHz and 5GHz.
2.4 GHz has a longer range, is better at going through obstacles (e.g., walls), and supports more devices. However, it can have a slower throughput, fewer channels and is often more congested than 5 GHz networks because other household devices also use the 2.4 GHz network band.
5 GHz on the other hand offers faster throughput, less congested channels, and more channels that don’t overlap. It has a shorter range compared to 2.4 GHz networks, doesn’t go through walls and other obstacles as well and is not as widely used by other devices.
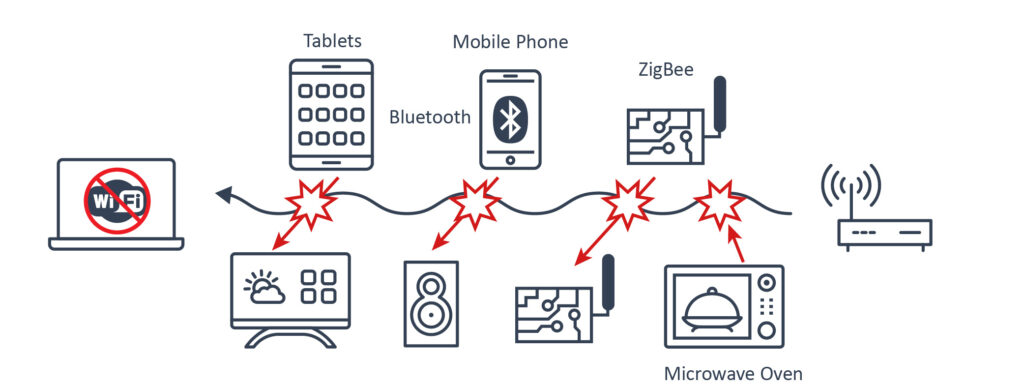
Stop using Bluetooth
Did you know that using Bluetooth headphones can interfere with your Wi-Fi bands? This is especially true for Wi-Fi networks based on the 2.4GHz frequency band, which is standard for most routers. This is because Bluetooth operates at the same 2.4GHz frequency band and signal overlap is possible. Although Bluetooth and Wi-Fi networks have systems in place to tackle interference, it still does occur on rare occasions. The effect of Bluetooth interference on wi-fi connection results in degraded network performance, including slow speeds.
Still not working?
You can try any of these tips to improve the quality of your video calls:
Wired connection
If your Internet router has an option for a wired connection, join with a wired option versus a wireless connection.
Disable HD video
You can disable the HD video option by selecting video settings in a meeting – select the up arrow to the right of the video icon and check or uncheck the HD video option.
Mute microphone, disable video
When you aren’t talking mute your audio (click on the microphone icon to mute or unmute) or disable your video. This will stop Zoom needlessly uploading your audio or video when you’re not speaking.
Close other applications
Zoom and Teams both use memory and processing from your computer and are not prioritised over other applications. Closing applications you do not need will improve your video conferencing experience.
Use a Wi-Fi extender
Purchase a Wi-Fi extender to increase the distance and strength of your Wi-Fi signal
Use mobile hotspot
Believe it or not, sometimes you may have a more reliable connection on your phone or using your phone as a mobile hotspot. You should be able to reach download speeds of between 20Mbps and 100Mbps on a 4G connection, which is more than enough for Zoom.

We hope these tips help improve the reliability of your next video conferencing call. Just remember, it might not be you that’s the problem. Even if everything’s good at your end, the other participant might have a problem with their connection. If that’s the case, do them the kindness of sharing this article on how to fix bad quality videos. By improving one person’s bandwidth or connectivity issues, you’ll ultimately enhance the meeting for your whole team. Better video quality lends itself to clearer communication, stronger teamwork and greater results overall.
If you or your company are in search of a premium video conferencing platform, check out our range of carts designed to bring teleconferencing wherever you need it.







